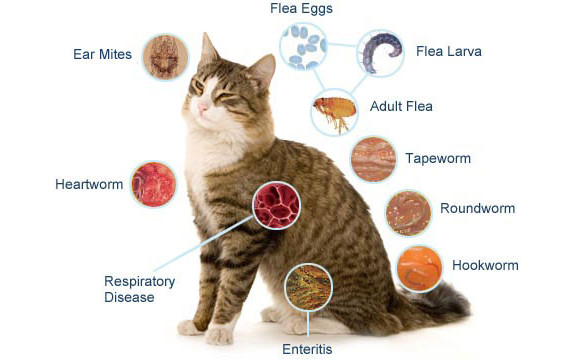
Cats, like all pets, are susceptible to various diseases. However, many of these conditions are preventable with proper care and vigilance. This guide delves into common preventable diseases in cats, their symptoms, prevention strategies, and treatment options, offering cat owners valuable insights into maintaining their feline friends’ health.
1. Feline Upper Respiratory Infections (URI)
Causes: URIs in cats are primarily caused by viruses like feline herpesvirus (FHV-1) and feline calicivirus (FCV), often complicated by secondary bacterial infections.
Symptoms: Sneezing, nasal discharge, coughing, eye discharge, fever, and loss of appetite.
Prevention: Vaccination is the most effective preventive measure. Maintaining a clean environment and minimizing stress can also help prevent infections.
Treatment: Antibiotics for secondary bacterial infections, antiviral medications, and supportive care such as hydration and nutritional support.
2. Feline Panleukopenia (Feline Distemper)
Causes: Feline panleukopenia virus (FPV), a highly contagious and often fatal virus affecting cats.
Symptoms: Vomiting, diarrhea, severe dehydration, lethargy, and sudden death in severe cases.
Prevention: Vaccination is crucial. Isolate infected cats to prevent the spread of the virus.
Treatment: Supportive care including fluids, electrolytes, and antibiotics to prevent secondary infections.
3. Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV)
Causes: FeLV, a retrovirus that suppresses the immune system, making cats more susceptible to infections and certain cancers.
Symptoms: Weight loss, fever, lethargy, anemia, and persistent infections.
Prevention: Vaccination and keeping cats indoors to reduce exposure to infected cats. Regular testing is recommended for at-risk cats.
Treatment: There is no cure, but supportive care and managing secondary infections can improve the quality of life.
4. Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV)
Causes: FIV, a virus similar to HIV in humans, spread through bite wounds.
Symptoms: Recurrent infections, weight loss, fever, and enlarged lymph nodes.
Prevention: Keep cats indoors to avoid fights with FIV-positive cats. Regular testing and neutering to reduce aggressive behavior.
Treatment: No cure exists, but supportive care and treating secondary infections can help manage the disease.
5. Rabies
Causes: Rabies virus, typically spread through bites from infected animals.
Symptoms: Behavioral changes, aggression, excessive salivation, paralysis, and death.
Prevention: Vaccination is the best prevention. Keeping cats indoors and away from wild animals reduces the risk.
Treatment: There is no treatment for rabies once symptoms appear, making prevention through vaccination critical.
6. Feline Infectious Peritonitis (FIP)
Causes: Feline coronavirus (FCoV), which can mutate into the more harmful FIP virus.
Symptoms: Weight loss, fever, abdominal swelling, and neurological signs.
Prevention: Reducing stress and overcrowding in multi-cat environments. Good hygiene and sanitation practices can help prevent the spread of FCoV.
Treatment: No definitive cure exists, but experimental treatments and supportive care can sometimes manage symptoms.
7. Heartworm Disease
Causes: Dirofilaria immitis, a parasitic worm transmitted by mosquitoes.
Symptoms: Coughing, difficulty breathing, weight loss, and lethargy.
Prevention: Monthly heartworm preventive medications are the best protection.
Treatment: There is no approved treatment for heartworms in cats, making prevention crucial.
8. Ringworm
Causes: Fungi such as Microsporum canis, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, and Microsporum gypseum.
Symptoms: Circular patches of hair loss, scaly or crusty skin, and itching.
Prevention: Maintaining good hygiene and regular veterinary check-ups. Quarantine and treat infected cats to prevent the spread.
Treatment: Antifungal medications, both topical and oral, and environmental cleaning.
9. Dental Disease
Causes: Plaque and tartar buildup leading to gingivitis and periodontal disease.
Symptoms: Bad breath, red or swollen gums, difficulty eating, and tooth loss.
Prevention: Regular dental check-ups, professional cleanings, and daily tooth brushing.
Treatment: Professional dental cleaning, tooth extractions if necessary, and antibiotics for infections.
10. Obesity
Causes: Overfeeding, lack of exercise, and genetic predisposition
Symptoms: E
Prevention: Bal
Treatment:
Conc
Preventing common diseases in cats involves a combination of regular veterinary care, vaccinations, proper nutrition, and maintaining a clean and stress-free environment. By staying vigilant and proactive, cat owners can ensure their feline friends lead healthy and happy lives.
For more information on preventing common cat diseases, visit the original article on Cats Place.